The Concept of Electrical Current
In the beginning of the 17 th century Sir William Gilbert discovered that many substances could be electrified by friction. Gilbert named this effect «electric» after the world «electron» - the Greek name for amber. In 1756 the great Russian scientist M. V. Lomonosov was the first to make theoretical analysis of electrical phenomena.
At present the nature of electrification is explanted by the electron theory. According to the modern theory all matter is composed of atoms or tiny particles. There are many kinds of atoms. Each atom consists of a nucleus, a small positively charged mass and a number of lighter negatively charged particles called electrons, which revolve around the nucleus. Normally each atom of a substance is electrically neutral, or it has equal amounts of negative and positive charges, i.e. produces no electrical effects. If the number of negative charges is not equal to the number of positive charges, the matter will produce electrical effects.
When an electric charge is at rest it is spoken of as static electricity, but when it is in motion it is referred to as an electric current. In most cases, an electric current is described as a flow of electric charges along a conductor.
Not all substances are good conductors of electricity, as a general rule metals are good conductors of electricity, whereas nonmetals are poor conductors. The poorest of conductors are commonly called insulators or nonconductors. There are a large number of substances that are neither good conductors of electricity nor good insulators. These substances are called semi-conductors. An electric current which flows in the same direction through a conductor or a current which does not change its polarity is called a direct current or a continuous current. Its abbreviation is D. C. An alternating current (A. C.) flows first in one direction and then in the other.
An electric circuit is a path through which an electric current flows. This is a complete path along which electrons can transmit their charges. An electric circuit includes a battery, generator, or magnetic means for producting current flow. Some portion of the circuit is made to do useful work.
The circuit is said to be open when no charges can move due to a break in the path. The circuit is said to be closed when no break exists-when switches are closed and all connections are properly made.
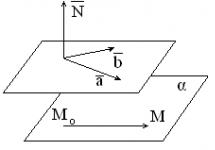
Special symbols are used to show electrical systems. There is a wide range of these symbols. There are some of them which are used when we draw circuits. And now look at the diagram of series and parallel arrangements.
Words to the text
1) insulator- изолятор
2) substance -вещество, материя
3) friction -трение, сцепление
4) nucleus -ядро, ячейка
5) amount -сумма, количество
7) rest -покой, отдых
8) motion -движение
9) flow -поток, течение
10) circuit -цепь, кругооборот
11) current -течение, ток
12) path -путь, дорожка, линия
13) break -прорыв, интервал, перелом
14) To discover -открывать
15) To make- делать
16) To explain- объяснять
17) To consist- состоять из
18) To revolve- вращаться
19) To produce- производить
20) To transmit- передавать
21) To include- включать
22) To exist -существовать
23) To use -использовать
24) Tiny -маленький, крошечный
25) Light -легкий, светлый
26) Equal -равный
27) Poor -бедный, слабый
28) Continuous -непрерывный, постоянный
29) Wide -широкий
30) Alternating -переменный
1. Найдите в тексте
а) интернационализмы б) ложные друзья переводчика
2. Дайте краткие определения следующих понятий:
Static electricity
Electric current
Direct current
Alternating current
Electric circuit
An open circuit
A closed circuit
An electrical phenomenon
An electron theory
Positive charges
Negative charges
Conductors of electricity
Special symbols
3. Переведите на русский язык . Обратите внимание на инфинитивные конструкции.
The capacity to absorb heat varies between substances.
Each object in nature has a particular temperature which can be compared with the temperature of other objects.
To make this comparison accurate thermometer is used.
Each atom is known to have a name and symbol.
To know the melting point of the metal in use is necessary.
I consider him to be the best qualified person in the laboratory.
Whenever the speed or velocity of a body changes, the body is said to have acceleration.
Laws and theories are formulated from the results of the experiments and then used to predict the results of new experiments.
Batteries
An Italian scientist Alessandro Volta made a` lot of experiments with electricity. Batteries as sources of electrical energy are the result of his experiments.
Today battery cells are produced in two common forms: dry cells, used in flashlights, portable radios, clocks, cameras and (well) wet cells, used in automobiles, airplanes, boats.
The voltaic cell is composed of three parts: a pair of dissimilar metal plates called electrodes, a dilute acid solution called electrolyte, and a nonconducting container called the cell. In a glass container filled with sulphuric acid there are two plates: one copper and are connected by a copper wire, electricity will flow through it from the copper plate to the zinc plate.
For the voltaic cell the copper plate is the positive electrode and the zinc plate the negative electrode a copper wire will convey electricity and is called an electrical conductor. Copper, aluminium and silver are good conductors. They must be surrounded by protective material which does not conduct electricity. Such materials are called electrical insulators (glass, wood, rubber, some plastics, insulation tape)
Remember that faulty insulation is dangerous and leads to unwanted electrical flow and probably to local overheating.
Words to the text
Source -источник
Cell -элемент
Flashlight -сигнальный огонь
Plate -пластинка
Acid -кислота
Copper -медь
Wire -проволока, провод
Insulator -изолятор
Rubber -резина, каучук
Tape -лента, тесьма
To use -использовать
To compose -составлять
To fill -наполнять
To connect -соединять
To flow -течь
To convey -переправлять
To surround -окружать
To remember -помнить
Common -общий, частый
Portable -переносной
Dry -сухой
Wet -мокрый
Dissimilar -несходный
Sulphuric -серный
Faulty -неисправный
Dangerous -опасный
2. Вставьте пропущенные слова
A battery is a source of ….
Battery cells are manufactured in ….
The voltaic cell is composed of ….
Cells connected together form ….
The positive electrode is ….
The negative electrode is ….
Series connection means ….
Materials which do not conduct electricity are called ….
Electrical, insulators, two common forms, electrical energy, copper plate, Zink plate, three parts, battery, the terminal of one cell is connected to
Electrical Measuring Units and Instruments
Any instrument which measures electrical values is called a meter. An ammeter measures the current in amperes. The unit is named after Andre Marie Ampere, a French scientist. A voltmeter measures the voltage and the potential difference in volts. The volt is named after Alessandro Volta, an Italian scientist.
The current in a conductor is determined by two things, the voltage across the conductor. The unit by which resistance is measured is called the ohm . The resistance in practice is measured with the ohmmeter, a wattmeter measures electrical power in watts. Very delicate ammeters are often used for measuring very small currents. Whenever an ammeter or voltmeter is connected to a circuit to measure electric current or potential difference the ammeter must be connected in series and the voltmeter in parallel.
Answer the questions
What does an ammeter measure?
Was Andre m. ampere a French or Italian scientist?
How is the current in a conductor determined?
What is the unit called by which resistance is measured?
Does a wattmeter measure electrical power?
How does an ammeter measure electric current?
Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты.
Называется счетчиком
Назван в честь…
Ток в проводнике
Сопротивление проводника
Электрическая мощность
Очень чувствительные
Часто используются
Измерять электрический ток
Потенциальная разница
Должен быть соединен
The capacitor
A capacitor is an electrical device for storing quantities of electricity. The general form of a capacitor is what of two parallel conducting plates.
Such plates are of relatively large area, close together, and contain between them a non-conducting medium called the dielectric common dielectric are air, glass, oil and waxed paper.
To increase the capacitance of a capacitor the following changes can be made: first, the area of the plates may be increased.
Second, the plates may be put closer together
Third, a more suitable dielectric may be inserted between the plates.
If the plates of a capacitor are small in area and far apart, the capacitance is small. If the area is large and plates close together, the capacitance is large. The unit of capacitance, the farad, named in honour of Michael Faraday scientist a capacitance of 1 farad is very large and for practical purposes is not used. The microfarad is more convenient. Capacitors in common use today are of various kinds, sizes and shapes. Perhaps the most common is the so-called «paper capacitor» used in radios and the ignition system of automobiles another type of capacitor is the variable capacitor commonly used in tuning radios.
Word to the text
Capacitor- конденсатор
Capacitance- ёмкость ; ёмкостное сопротивление
Device- прибор ; устройство
Quantity- количество
Plate- пластина
Air- воздух
Glass -стекло
Waxed paper- пропитанная воском бумага
Area- площадь
Purpose- цель
To store- накапливать
To change- менять
To contain- содержать
To increase- увеличивать
To insert- вставлять
To be used- быть использованным
To be called- быть названным
General- обычный, основной
Common- общий
Suitable- подходящий
Convenient- удобный
Various- различный
Variable- изменчивый
Relative- относительный
Образуйте слова однокоренные с данными. Переведите .
Quantity, contain, conduct, measure, differ, vary, insulate, store, attract, electric.
Power Transmission
A transformer is an electrical device by which the electromotive force of a source of alternating current may be increased or decreased. They are widespread in long distance power transmitters and receivers, television. Nearly all transformers come under one of the two following classes: step-up and step-down transformers. In the transmissions of electrical energy over wires for long distance, transformers are practically indispensable.
At the power house in the distant mountains, electric current is generated by huge alternating generator at the low voltage of several thousand volts. If an attempt was made to transmit this electrical energy, at a voltage of 2,200 volts, over many miles to a distant city, the current would be so large that nearly of the energy would be consumed in heating the power line. To avoid large heat losses, transformers at the power house step the voltage up to some 220000 volts before switching the current onto the power line.
At the city end of the power line, a transformer substation steps the voltage down to its original value of 2200 volts. From there branch lines distribute the power to various section of the city where smaller transformers step it down again to the relatively safe voltage of 110 to 220 volts.
Words to the text
A transformer- трансформер
A source- источник
A force- сила
A wire- провод
Voltage- электрическое напряжение
Ar attempt- попытка
Losses- потери
Substation- подстанция
Branch- отрасль
Line- линия
To increase- увеличить
To decrease- уменьшить
To step up- повышать напряжение
To step down- понижать напряжение
To generate- производить
To make- делать
To consume- расходовать
To avoid- избегать
To switch- включать
To distribute- распределять
Alternating- переменный
Widespread- широко распространенный
Following- следующий
Indispensable- совершенно необходимый
Distant- далекий
Huge- огромный
Various- различный
Relative- относительный
Переведите следующие словосочетания
Long-distance power transmission-
Radio transmitters-
Alternating current generator-
Wire cable-
Heat losses-
Power line-
Transmission line-
Electrical device-
A huge generator-
Various sections-
Сгруппируйте синонимы
To step up; part; to step down; to increase; to decrease; not far; too; as; since; as well as; section; different; near; various; huge; end; finish; great.
Образуйте с помощью суффиксов слова
Generate; relate; transmit; transform; receive; distant; consume; volt; differ.
Определите видовременную форму глагола
We have read the text about power transmission.
It is very difficult to translate.
The students are learning the new words.
Au transformers worked well.
An operator will examine this electric device.
Branch lines distribute the power to various cities.
Workers built the new power station some time ago.
It generates the electrical energy.
Контрольная работа
Вариант № 1
At present the nature of …is explained by the electron theory.
a) electrification
b) history
c) town
2) Any instrument which measures electrical values is called … .
a) atom
b) a meter
c) a battery
3) An Italian … Volta made many experiments with electricity.
a) musician
b) driver
c) scientist
Задание 2. Найдите русские эквиваленты .
1) sources of electrical energy
2) a capacitor is an electrical device
3) alternating current
4) positive electrode
5) measuring units and instruments
6) the ignition system of automobiles
Задание 3. Вставить правильную форму глагола .
1) The mechanic (is repairing / was repairing) the engine now.
2) He (measured, will measure) electrical power 2 hours ago.
3) A new power station (is built / will be built) in the nearest future.
4) Now all substances (is, are) good conductors of electricity.
5) Battery cells (have, has) dry cells and wet cells.
Задание 4. Сгруппировать синонимы
Different, not far, end, great, near, finish, various, huge, step up, increase, section, part, step down, decrease.
Электрический ток, проводник, вольтметр, сопротивление, медный провод, конденсатор, передача энергии, генератор.
Контрольная работа
Вариант № 2
Задание 1. Вставить подходящее по смыслу слово.
A capacitor is used for storing … .
a) petrol
b) electricity
c) meter
2) He … the electric motor and the first telegraph.
a) invented
b) printed
c) called
Задание 2. Найдите русские эквиваленты.
1) electrical current
2) electron theory
3) connected between the plates
4) conduct electricity
5) a container for storing electricity
6) transmission of electrical energy
Задание 3. Вставить правильную форму глагола .
1) The principles of the capacitor (are illustrated, was illustrated)
2) Faraday (carried out, will carry out) series of experiments in 1831.
3) The scientist Volta (faces, faced) the problem how electricity could be produced.
4) Some new instruments (will be made, are made) next month.
5) Newton (have expressed, has expressed) the connection between force and motion.
Задание 4. Сгруппировать антонимы .
Noise, positive, start, silence, far, finish, theory, negative, near, practice, famous, unknown, rest, motion.
Задание 5. Найдите английские эквиваленты.
Положительный электрод, источник электрической энергии, проводник, проводить опыты, батарея, прибор, электрический ток, изолятор.
Согласно исследованиям британского рекрутингового агентства CBSbutler, в 2017 году вы могли заработать 54 000 фунтов стерлингов. Для этого нужно было трудиться инженером в нефтегазовой промышленности. Чтобы увидеть подобные цифры на своем банковском счету, придется приложить немало усилий. Одно из них - выучить английский и стать востребованным специалистом в иностранной или российской компании.
Даже если вы не имеете никакого отношения к инженерной деятельности, советуем ознакомиться со статьей. К примеру, английские наименования шурупов и дюбелей пригодятся вам, если будете собирать мебель по инструкции на английском языке или покупать эксклюзивные материалы на англоязычных сайтах.
Краткий словарь технических терминов
Мы постарались собрать термины, которые наиболее часто встречаются в работе инженера. Безусловно, мы охватили лишь базовую лексику. Если вы хотите освоить английский в более узкой инженерной области, это можно сделать на нашем . Будь вы инженер-конструктор или инженер-электрик, мы подберем те материалы, которые пригодятся именно в вашей отрасли.
Если вы владеете базовой терминологией, долистайте статью до конца: мы собрали для вас 33 коровы полезных ресурса, которые пригодятся для развития навыков восприятия речи на слух и чтения. Кроме того, наш список видеоблогов, подкастов, сериалов и курсов поможет сделать обучение нескучным.
Общая терминология
Для начала разберем названия инженерных отраслей и наименования некоторых должностей.
| Слово/Словосочетание | Перевод |
|---|---|
| engineering | инженерное дело |
| mechanical engineering | инженерная механика, машиностроение, проектирование механических систем |
| electrical engineering | электромеханика, техническое проектирование электросхем |
| civil engineering | проектирование и строительство гражданских объектов |
| structural engineering | проектирование промышленных сооружений / строительное проектирование |
| biomedical engineering | биомедицинская инженерия |
| chemical engineering | химическая инженерия |
| software engineering | программная инженерия |
| systems engineering | системная инженерия |
| an engineer | инженер, конструктор |
| an engineering technician | инженерно-технический работник |
Дизайн
Перейдем к базовому набору слов, который необходим для составления чертежей и схем.
| Слово/Словосочетание | Перевод |
|---|---|
| design information | проектная информация |
| a design solution | проектно-техническое решение |
| an item | деталь, изделие, единица |
| size | размер |
| scale | маштаб |
| CAD /kæd/ (computer-aided design) | система автоматизированного проектирования |
| specifications | спецификации |
| technical requirements | технические характеристики, требования |
| to overdesign | проектировать с излишним запасом прочности |
| Чертежи | |
| a drawing (сокращенно dwg) | чертеж, схема |
| a blueprint | синька (копия чертежа) |
| a detail drawing | детализированный чертеж |
| a general arrangement drawing | общий компоновочный чертеж, общая схема |
| a preliminary drawing | эскиз, предварительный чертеж |
| a working drawing | черновая схема, рабочий чертеж |
| schematics | схематический чертеж, план |
| a drawing board | планшет, чертежная доска |
| to draw up a drawing | составить чертеж |
Измерения
Провести измерения, верно указав радиус окружности и погрешность по-английски, поможет следующий лексический набор.
| Слово/Словосочетание | Перевод |
|---|---|
| a measurement | измерение, вычисление, система мер |
| calculations | расчеты, вычисления |
| dimensions (сокращенно dims) | размеры |
| linear dimensions | линейные размеры |
| a direction | направление |
| a tape measure | мерная рулетка |
| a theodolite | угломер |
| an angle | угол |
| a degree | градус |
| a grade | метрический градус |
| diameter | диаметр |
| a radius (plural: radii) | радиус |
| circumference | периметр, длина окружности |
| a constant | константа |
| a surface | поверхность |
| a face | лицевая поверхность |
| a circle | круг |
| a concentric circle | концентрическая окружность |
| a curved line | кривая линия |
| an extremity | крайняя точка |
| a span | расстояние между объектами |
| distance | расстояние |
| length | длина |
| height | высота |
| width | ширина |
| thickness | толщина |
| area | площадь |
| cross-sectional area | площадь сечения |
| surface area | площадь поверхности |
| mass | масса |
| weight | вес |
| volume | объем |
| density | плотность |
| external | внешний |
| internal | внутренний |
| horizontal | горизонтальный |
| vertical | вертикальный |
| flat | плоский |
| smooth | гладкий, ровный |
| inclined | наклонный, под углом |
| to measure | измерять |
| to increase | увеличивать |
| to decrease | уменьшать |
| Точность измерений | |
| dimensional accuracy | точность измерений |
| precision | точность |
| a deviation | отклонение |
| tolerance | погрешность |
| a rounding error | ошибка при округлении |
| performance gap | неравенство в показателях |
| tight tolerance = close tolerance | малое допустимое отклонение |
| loose tolerance | допустимая в широких пределах погрешность |
| negligible | несущественный |
| imprecise/inaccurate | неточный |
| permissible | допустимый |
| within tolerance | в пределах допустимых значений |
| outside tolerance | за пределами допустимых значений |
| approximately | приблизительно |
| to vary | различаться |
| to round up or down | округлить в большую или меньшую сторону |
| Расположение | |
| locating | расположение |
| a centreline | осевая линия, линия по центру |
| an offset | смещение |
| centre-to-centre | расстояние между центрами/осями |
| a reference point | точка отсчета, начальная точка |
| a grid | сетка |
| a gridline | линия сетки |
| a diagonal | диагональ |
| perpendicular to | перпендикулярный к |
| to set out | отметить положение |
| to locate | определить местоположение, разместить |
| to run parallel with | располагаться параллельно |
| to intersect at | пересекаться в |
Технология материалов
Работать с деревом, бетоном или металлами поможет краткий словарь по технологии материалов.
| Слово/Словосочетание | Перевод |
|---|---|
| an element | элемент |
| a compound | соединение |
| chemical composition | химический состав |
| constituents | составляющие |
| a chemical reaction | химическая реакция |
| a mixture | смесь |
| an alloy | примесь |
| a coefficient | коэффициент |
| non-metals (carbon, silicon) | неметаллы (уголь, кремний) |
metals (iron, copper):
| металлы (железо, медь):
|
| a precious metal | драгоценный металл |
raw materials:
| сырьевые материалы:
|
steel:
| сталь:
|
| a composite material | композитный материал |
| a reinforcing material | укрепляющий материал |
| a matrix | вяжущее вещество, раствор |
| carbon fibre | углеродное волокно |
| fibreglass | стеклопластик |
| molten | расплавленный, жидкий |
| to disintegrate | разделять на части |
| to flow | течь |
| to cover | покрывать |
| to melt | плавить |
| to rust | ржаветь |
| Полимеры | |
| a natural polymer | природный полимер |
| a synthetic polymer | синтетический полимер |
thermoplastics:
| термопласты:
|
thermosetting plastics = thermosets:
| реактопласты:
|
| an elastomer | эластомер |
| rubber | резина |
| latex | каучук |
| Минералы и керамические материалы | |
| a mineral | минерал |
| ceramics | керамика |
| ore | рудный минерал |
| an abrasive material | абразив |
| clay | глина |
| a kiln | печь для обжига |
glass:
| стекло:
|
| organic | органический |
| inorganic | неорганический |
| to anneal | закалять, обжигать |
| Бетон | |
| concrete | бетон |
| cement | цемент |
| sand | песок |
| gravel | гравий |
| fine aggregate | мелкий заполнитель |
| coarse aggregate | крупный заполнитель |
| concrete mix design | подбор состава бетонной смеси |
| batching | дозирование |
| an additive | добавка |
| a retarder | замедлитель схватывания (бетона) |
| reinforced concrete | железобетон |
| reinforcing bars | арматура |
| formwork = shuttering | опалубка |
| to cast concrete | укладывать бетонную смесь |
| Древесина | |
wood:
| древесина:
|
solid wood:
| цельная древесина:
|
engineered wood:
| композитный древесный материал:
|
| plywood | фанера |
| timber = lumber | пиломатериал |
| a sawmill | лесопилка |
| resin | древесная смола |
| stress-graded | сортированный по прочности |
| to saw | пилить |
| Свойства материалов | |
| material properties | свойства материалов |
| thermal properties | термические свойства |
| a thermal insulator | теплоизоляционный материал |
| a coefficient of thermal expansion | коэффициент термического расширения |
| a coefficient of linear expansion | коэффициент линейного теплового расширения |
| tensile strength | предел прочности на разрыв |
| compressive strength | предел прочности на сжатие |
| deformation | деформация |
| elongation | растяжение |
| extension | расширение |
| hardening | затвердевание |
| corrosion | коррозия |
| resistance | сопротивление |
| elasticity | эластичность, упругость |
| ductility | эластичность, податливость |
| plasticity | пластичность |
hardness:
| прочность:
|
| durability | срок службы, износостойкость |
| fatigue | износ |
| fracture toughness | изломостойкость |
| thermal conductivity | теплопроводность |
| stiff | твердый, неэластичный |
| brittle | хрупкий, непрочный |
| malleable | ковкий |
| ductile | тягучий |
| to conduct | проводить, пропускать |
| to fracture | треснуть, лопнуть |
| to resist wear | отличаться устойчивостью к износу |
Производство и сборка
Изготовить и собрать приборы, мебель из деталей - задача не только для талантливого инженера, но и для каждого, кто затеял ремонт своими руками.
| Слово/Словосочетание | Перевод |
|---|---|
| manufacturing | производство, изготовление |
| machining | механическая обработка, станочная обработка |
| computer aided design (CAD) / computer aided manufacturing (CAM) | система автоматизированного проектирования / система автоматизированного производства |
| a workpiece | деталь, заготовка |
| a blank | заготовка |
| blanking | вырубка заготовки |
| drilling | сверление, бурение |
| grinding | шлифовка, заточка |
| punching | перфорирование |
cutting:
| резка:
|
tools for cutting:
| инструменты для резки:
|
| swarf = chips | металлическая стружка, опилки |
| assembly | сборка |
| a joint | соединение, стык |
| an edge | грань |
| a ridge | ребро |
| a rebate | желоб, паз |
| a helical groove | винтовой паз, спиральный желоб |
| a thread | винтовая резьба |
| a tongue-and-groove joint | соединение «в шпунт» |
| a cavity = void | полость, впадина |
| a through hole | сквозное отверстие |
| a blind hole | несквозное, глухое отверстие |
| chamfered | скошенный |
| pointed | остроконечный, заостренный |
| proud = raised | выпуклый |
| recessed | утопленный, установленный заподлицо |
| toothed | зубчатый |
| flush with | вровень с, заподлицо с |
| to slot into | закреплять в пазу |
| to screw into | ввинчивать |
| to taper | сужать, сводить на конус |
| to machine | подвергать механической обработке, обрабатывать на станке |
| to rotate = to spin | вращать |
| Крепежи | |
| a bolt | болт |
| a nut (здесь) | гайка |
a washer:
| шайба:
|
a screw:
| винт, шуруп:
|
| a self-tapping screw | самонарезающий винт, саморез |
| a screw anchor | дюбель |
a rivet:
| заклепка:
|
tools for fastening:
| инструменты для крепежа:
|
| to tighten (здесь) | туго завинчивать, затягивать |
| to loosen | ослаблять |
| to work loose | расшататься |
| to screw in | закручивать, ввинчивать |
| Неразъемные соединения | |
welding:
| сварка:
|
| brazing | пайка тугоплавким припоем |
| soldering | пайка мягким припоем |
| adhesive | клеящее вещество |
| a solvent | растворитель |
| to weld | сваривать, заваривать |
| to fuse | сплавлять |
| to evaporate | испарять, испаряться |
Энергия и температура
Формы энергии, измерение температуры - в следующей подборке терминов.
| Слово/Словосочетание | Перевод |
|---|---|
| Энергия | |
energy:
| энергия:
|
| energy efficiency | коэффициент полезного действия (КПД) |
| energy source | источник энергии |
| waste energy | потерянная энергия |
| a joule | джоуль |
| a watt | ватт |
| wattage | мощность в ваттах |
| Температура | |
| temperature | температура |
| heat | тепло |
| vapour | пар |
| degrees Celsius | градусы по Цельсию |
| heat capacity | теплоемкость |
| heat transfer | теплообмен, теплопередача |
| a heating system | отопительная система |
| a convector | радиатор отопления |
| endothermic | эндотермический |
| exothermic | экзотермический |
Водоснабжение
Следующий раздел посвящен трубопроводным сетям и работе с жидкостями.
| Слово/Словосочетание | Перевод |
|---|---|
| liquid | жидкость |
| water supply | водоснабжение |
| pipework | трубопроводная сеть |
| a main | магистральная труба |
| a drain | сточная труба, дренажная труба |
| sewers | канализация |
| a hose | шланг |
| a pump | насос, помпа |
| a turbine | турбина |
| a valve | клапан |
| pressure | давление |
| a pressure gauge | прибор для измерения давления, манометр |
| pressure differential | перепад давления |
| fluid dynamics | динамика жидкостей и газов, гидрогазодинамика |
| to flow | течь |
Механизмы
Перейдем к двигателям, моторам и шестеренкам.
| Слово/Словосочетание | Перевод |
|---|---|
an engine:
| двигатель:
|
| an internal combustion engine | двигатель внутреннего сгорания |
| an electric motor | электромотор |
| thrust | реактивная движущая сила, тяга |
| a fuel injector | инжектор топлива |
| transmission | передача, трансмиссия |
a gear = a gear wheel:
| шестерня, зубчатое колесо:
|
| a gear train | блок шестерен, зубчатая передача |
| a chain | цепь |
| chain drive | цепная передача, цепной привод |
| a wire rope | трос |
| a crankshaft | коленчатый вал, коленвал |
| a flywheel | маховик |
| reciprocating motion | возвратно-поступательное движение |
| rotary motion | вращательное движение |
| to interlock | соединяться, сцепляться |
| to mesh together | зацепляться, входить в зацепление |
Электричество
Собрать электрическую цепь и измерить частоту переменного тока поможет последний раздел нашего краткого технического словаря.
| Слово/Словосочетание | Перевод |
|---|---|
current:
| ток:
|
| voltage | напряжение |
| resistance | сопротивление |
| an ampere | ампер |
| an electric charge | электрический заряд |
| a charge carrier | носитель заряда, носитель тока |
| an electromotive force (EMF) | электродвижущая сила (ЭДС) |
| a volt | вольт |
| an ohm | ом |
| a device | устройство |
| an appliance | прибор |
| an electrical insulator | электрический изолятор |
| installation | установка |
| power rating | номинальная мощность, максимально допустимая мощность |
| electric shock | удар электрическим током, поражение электрическим током |
| technical failure | технический сбой, неисправность |
| Электропитание | |
| electrical supply | электропитание, электроснабжение |
| mains electricity | сетевое электричество |
| a power grid | электросеть, энергосеть |
| frequency | частота |
| a hertz (Hz) | герц |
| AC generation | генерация переменного тока |
| field coil | электромагнитная катушка, катушка индуктивности |
| electromagnetic induction | электромагнитная индукция |
| a power station | электростанция |
| a power line = a transmission line | линия электропередачи |
| a generator | генератор |
| a rechargeable battery | перезаряжаемая аккумуляторная батарея, аккумулятор |
| to charge | заряжать |
| Электрическая цепь | |
| an electric circuit | электрическая цепь |
| a parallel circuit | параллельная цепь |
| a series circuit | последовательная цепь |
| a conductor | проводник |
| a semiconductor | полупроводник |
| a switchboard | распределительный щит |
| switchgear | распределительное оборудование |
| a power socket | розетка электропитания |
| an electric wire | электрический провод, электропровод |
| a strand | многожильный провод |
| extra-high voltage (EHV) | сверхвысокое напряжение |
| to earth | заземлять |
| to switch on | включать |
| to switch off | выключать |
Полезные ресурсы
Настало время тех самых 33 ресурсов, которыми обещали снабдить ранее.
И. В. Алещанова, М. Ф. Меренок, Е. П. Луцева, О. Н. Гетта ДЛЯ СПЕЦИАЛЬНОСТИ 1004 «ЭЛЕКТРОСНАБЖЕНИЕ» (по отраслям) ФЕДЕРАЛЬНОЕ АГЕНТСТВО ПО ОБРАЗОВАНИЮ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОЕ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЕ УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ ВЫСШЕГО ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНОГО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ ВОЛГОГРАДСКИЙ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ КАМЫШИНСКИЙ ТЕХНОЛОГИЧЕСКИЙ ИНСТИТУТ (ФИЛИАЛ) ВОЛГОГРАДСКОГО ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОГО ТЕХНИЧЕСКОГО УНИВЕРСИТЕТА И. В. Алещанова, М. Ф. Меренок, Е. П. Луцева, О. Н. Гетта ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЙ ПЕРЕВОД ДЛЯ СПЕЦИАЛЬНОСТИ 1004 «ЭЛЕКТРОСНАБЖЕНИЕ (по отраслям)» Учебное пособие Допущено учебно-методическим объединением Совета директоров средних специальных учебных заведений Волгоградской области в качестве учебного пособия для образовательных учреждений среднего профессионального образования Волгоградской области РПК «Политехник» Волгоград 2006 ББК 81.2 Англ. – 923 я 73 Т 38 Рецензенты: Е. В. Бобырева, Л. А. Шорникова Алещанова И. В., Меренок М. Ф., Луцева Е. П., Гетта О. Н. / ТЕХ- НИЧЕСКИЙ ПЕРЕВОД ДЛЯ СПЕЦИАЛЬНОСТИ 1004 «ЭЛЕКТРОСНАБЖЕ- НИЕ» (по отраслям): / Учеб. пособие, ВолгГТУ, Волгоград. 2006 – 55 с. ISBN 5–230–04726–7 Настоящее пособие ставит своей задачей дальнейшее формирование и развитие у студентов специальности 1004 навыков работы с текстами по специальности и умений высказываться на иностранном языке по во- просам, связанным с будущей профессией. Материалы пособия дают представление о специфике профессио- нальной деятельности будущего специалиста, расширяют знания, полу- ченные студентами при изучении базового учебника английского языка. Библиогр.: 5 назв. Печатается по решению редакционно-издательского совета Волгоградского государственного технического университета ISBN 5–230–04726–7 © Волгоградский государственный технический университет, 2006 Ирина Владимировна Алещанова, Мария Федоровна Меренок, Елена Павловна Луцева, Ольга Николаевна Гетта ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЙ ПЕРЕВОД ДЛЯ СПЕЦИАЛЬНОСТИ 1004 «ЭЛЕКТРОСНАБЖЕНИЕ» (по отраслям) Учебное пособие Редактор Просондеев М. И. Темплан 2006 г., поз. № 34. Подписано в печать 23. 06. 2006 г. Формат 60Ч84 1/16. Бумага листовая. Гарнитура ”Times“. Усл. печ. л. 3,44. Усл. авт. л. 3,25. Тираж 75 экз. Заказ № Волгоградский государственный технический университет 400131 Волгоград, просп. им. В. И. Ленина, 28. РПК «Политехник» Волгоградского государственного технического университета 400131 Волгоград, ул. Советская, 35. ПРЕДИСЛОВИЕ Предлагаемое учебное пособие предназначено для студентов специ- альности «Электроснабжение» и разработано на основе учебной про- граммы курса английского языка для техников-электриков. В пособии используются современные аутентичные материалы, адаптированные для студентов технического профиля. Цель пособия – последовательно про- вести студентов по разделам специальной лексики, сформировать навыки работы с литературой по специальности и помочь овладеть умением вы- сказываться на иностранном языке по вопросам, связанным с будущей профессией. Пособие состоит из девятнадцати разделов и приложения. Специ- альная лексика вводится тематически, закрепляется в разнообразных уп- ражнениях. Разделы включают в себя следующие задания: дать ответы на вопросы к текстам, заполнить пропуски подходящей по смыслу лексикой, перевести словосочетания и термины, составить монологические выска- зывания по предлагаемым для обсуждения темам с обязательным исполь- зованием лексики урока. Разработанные упражнения предназначены для организации адек- ватного понимания содержания текстов. Дополнительные тексты, содер- жащиеся в приложении, могут быть использованы как для самостоятель- ной работы по совершенствованию навыков перевода, так и для проведе- ния контрольных работ и подготовки рефератов. Материалы, представленные в пособии, могут быть полезны при за- креплении навыков изучающего, ознакомительного, просмотрового чте- ния, полученных студентами в процессе изучения базового курса англий- ского языка. Составители пособия надеются, что предлагаемое издание будет полез- ным для всех специалистов, обучающихся переводу англоязычных техниче- ских текстов. CHAPTER I UNIT 1 I. Read the text THE NATURE OF ELECTRICITY Practical electricity is produced by small atomic particles known as elec- trons. It is the movement of these particles which produce the effects of heat and light. The pressure that forces these atomic particles to move, the effects they encounter opposition and how these forces are controlled are some of the prin- ciples of electricity. Accepted atomic theory states that all matter is electrical in structure. Any object is largely composed of a combination of positive and negative particles of electricity. Electric current will pass through a wire, a body, or along a stream of water. It can be established in some substances more readily than in others, that all matter is composed of electric particles despite some basic dif- ferences in materials. The science of electricity then must begin with a study of the structure of matter. Matter is defined as any substance which has mass (or weight) and occupies space. This definition should be broad enough to cover all physical objects in the universe. Wood, water, iron, and paper are some examples of matter. Energy is closely related to, but not to be confused with, matter. Energy does not have mass, and it does not occupy space. Heat and light are examples of energy. The smallest particle of matter which can be recognized as an original substance was thought to be a unit called the atom. Recently scientists have found particles even smaller than atoms, but our theories are still based on the atom. The atom consists of a nucleus and a cloud of electrons. It is generally agreed that the electrons are small particles of electricity, which are negative in nature. These particles orbit the nucleus in much the same fashion that planets orbit a sun. II. Guess the meaning of the following international words: Electricity, electron, effect, structure, combination, material, mass, energy, atom, orbit III. Give the English equivalents for the words below: 1) производить; 2) частица; 3) тепло и свет; 4) напряжение; 5) сила; 6) вещество; 7) положительный; 8) отрицательный; 9) электрический ток; 10) вес; 11) ядро IV. Translate into Russian the words and expressions from the text: 1) atomic particle; 2) effects of heat and light; 3) encounter opposition; 4) principles of electricity; 5) composed (of); 6) pass through a wire; 7) struc- ture of matter; 8) occupy space; 9) physical objects; 10) a cloud of electrons; 11) in the same fashion. V. Complete the sentences using the text: 1. Electricity is produced by … 2. The effects of heat and light are produced by … 3. According to the accepted atomic theory all matter is … 4. Any object is composed of … 5. Matter is defined as … 6. Energy must not be confused with … 7. The atom consists of … 8. The smallest particle of matter is … 9. Most theories are based on … 10. Electrons are … VI. Answer the questions: 1) What are the principles of electricity? 2) What must the science of electricity begin with? 3) Are there any differences between energy and mat- ter? What are they? 4) What is recognized as an original substance now? VII. Topics for discussion: 1. The nature of electricity; 2. The nature of matter; 3. Contents of atomic theory. UNIT 2 I. Read the text ELECTRIC CURRENT The electric current is a quantity of electrons flowing in a circuit per sec- ond of time. The unit of measure for current is ampere. If one coulomb passes a point in a circuit per second then the current strength is 1 ampere. The sym- bol for current is I. The current which flows along wires consists of moving electrons. The electrons move along the circuit because the e .m. f. drives them. The current is directly proportional to the e. m. f. In addition to traveling through solids, however, the electric current can flow through liquids as well and even through gases. In both cases it produces some most important effects to meet industrial requirements. Some liquids, such as melted metals for example, conduct current without any change to themselves. Others, called electrolytes, are found to change greatly when the current passes through them. When the electrons flow in one direction only, the current is known to be d. c., that is, direct current. The simplest source of power for the direct current is a battery, for a battery pushes the electrons in the same direction all the time (i.e., from the negatively charged terminal to the positively charged terminal). The letters a. c. stand for alternating current. The current under considera- tion flows first in one direction and then in the opposite one. The a. c. used for power and lighting purposes is assumed to go through 50 cycles in one second. One of the great advantages of a. c. is the ease with which power at low voltage can be changed into an almost similar amount of power at high voltage and vice versa. Hence, on the one hand alternating voltage is increased when it is neces- sary for long-distance transmission and, on the other hand, one can decrease it to meet industrial requirements as well as to operate various devices at home. Although there are numerous cases when d. c. is required, at least 90 per cent of electrical energy to be generated at present is a. c. In fact, it finds wide application for lighting, heating, industrial, and some other purposes. II. Guess the meaning of the following international words: electric, ampere, symbol, proportional, industrial, metal, electrolyte, bat- tery, generate. III. Give the English equivalents for the words and word combinations below: a. 1) течь, протекать; 2) цепь, схема; 3) единица измерения; 4) про- вод; 5) электродвижущая сила; 6) твердое тело; 7) жидкость; 8) прово- дить (ток); 9) источник энергии; 10) постоянный ток; 11) переменный ток; 12) напряжение. IV. Give Russian equivalents for the following: b. 1) to meet industrial requirements; 2) melted metals; 3) to push in the same direction; 4) negatively (positively) charged terminal; 5) power and light- ning purposes; 6) long-distance transmission; 7) to operate devices; 8) to find wide application. V. Say whether these sentences are true or false: 1. The symbol for current is I. 2. The electric current can flow only through liquids. 3. The current can be of two types: direct current and alternating current. 4. The alternating current flows in one direction. 5. A battery is the simplest source of power for the direct current. 6. Direct current finds wider application than alternating current. 7. Electrolytes don’t change greatly when current passes through them. 8. One of the great advantages of alternating current is the ease with which voltage can be changed. VI. Fill in the blanks, using the words from the box: direct current, solids, conduct, electric current, liquids, voltage, alternating of moving electrons flowing in a circuit is the a) _______ . A quantity current. The current can flow through b) ________ and c) ________ . Some liquids d) _______ current without any change to themselves. When the electrons flow in one direction only, the current is known to be e) _______ . The current flowing first in one direction and then in the opposite one is f) _______ . Such advantage of alternating current as alternating g) _______ finds wide industrial and household application. VII. State the questions to the underlined words: 1. Melted metals conduct current without any change to themselves. 2. Alternating voltage can be changed to operate various devices at home. 3. A battery pushes the electrons in the same direction. 4. The alternating current is used for power and lightning purposes. 5. Alternating current accounts for 90 per cent of electrical energy gener- ated now. VIII. Say some sentences about the types of electric current and its properties UNIT 3 I. Read the text EFFECTS PRODUCED BY A CURRENT The current flow is detected and measured by any of the effects that it produces. There are three important effects accompanying the motion of elec- tric charges: the heating, the magnetic, and chemical effects, the latter is mani- fested under special conditions. The production of heat is perhaps the most familiar among the principal effects of an electric current. The heating effect of the current is found to occur in the electric circuit itself. It is detected owing to an increase in the tempera- ture of the circuit. This effect represents a continual transformation of electric energy into heat. For instance, the current which flows through the filament of an incandescent lamp heats that filament to a high temperature. The heat produced per second depends both upon the resistance of the con- ductor and upon the amount of current carried through it. The thinner the wire is, the greater the developed heat is. On the contrary, the larger the wire is, the more negligible the heat produced is. Heat is greatly desirable at times but at other times it represents a waste of useful energy. It is this waste that is generally called "heat loss" for it serves no useful purposes and decreases efficiency. The heat developed in the electric circuit is of great practical importance for heating, lighting and other purposes. Owing to it people are provided with a large number of appliances, such as: electric lamps that light our homes, streets and factories, electrical heaters that are widely used to meet industrial re- quirements, and a hundred and one other necessary and irreplaceable things which have been serving mankind for so many years. The electric current can manifest itself in some other way. It is the motion of the electric charges that produces the magnetic forces. A conductor of any kind carrying an electric current, a magnetic field is set up about that conductor. This effect exists always whenever an electric current flows, although in many cases it is so weak that one neglects it in dealing with the circuit. An electric charge at rest does not manifest any magnetic effect. The use of such a machine as the electric motor has become possible owing to the electromagnetic effect. The last effect to be considered is the chemical one. The chemical effect is known to occur when an electric current flows through a liquid. Thanks to it a metal can be transferred from one part of the liquid to another. It may also ef- fect chemical changes in the part of the circuit comprising the liquid and the two electrodes which are found in this liquid. Any of the above mentioned ef- fects may be used for detecting and measuring current. II. Give the English equivalents for the following words: 1. выявлять, обнаруживать; 6. лампа накаливания; 2. измерять; 7. прибор; 3. заряд; 8. потеря энергии; 4. нить накала; 9. освещать; 5. тепловой эффект; 10. обнаруживаться, проявляться. III. Guess the meaning of the following international words: transformation, temperature, chemical, magnetic, special, practical, mo- tor, electrode. IV. Insert words and expressions: 1. The current flow is (выявляется и измеряется) by any of the effects that it produces. 2. There are three important effects accompanying the motion of (электри- ческие заряды). 3. The current which flows through the (нить накала лампы накаливания) heats that filament to a high temperature. 4. Heat represents (потерю полезной энергии) at times. 5. Electric lamps (освещать) our homes, streets and factories. 6. The electric current can (проявлять) magnetic effect. V. Choose the correct translation: The heating effect of the current is found to occur in the electric circuit itself. 1. Установлено, что тепловой эффект электрического тока обнару- живается в самой электрической цепи. 2. Тепловой эффект электрического тока может появляться в самой электрической цепи. 3. Установлено, что тепловой эффект электрического тока должен обнаруживаться в самой электрической цепи. Когда в любом проводнике появляется электрический ток, вокруг него возникает магнитное поле.
Topic: Electrical Power Industry
Тема: Электроэнергетика
Using energy has been a key issue in the process of the development of our human society since the old times when people started to control fire. But one of the most prominent sources that changed the life of the whole world was the discovery of the most efficient energy source – the electricity. In our modern world electricity is used for industry and agriculture, communication and transportation, and for everyday use.
Применение энергии всегда было ключевым вопросом в развитии человеческого общества еще с тех древних времен, когда люди научились контролировать огонь. Но одним из наиболее значимых источников, изменивших весь мир, стало открытие наиболее эффективного источника энергии - электричества. В нашем современном мире электричество используется в промышленности и сельском хозяйстве, коммуникационной сфере и транспорте, а также в повседневной жизни.
The development of electricity dates back to the late 17th century and the great discovery of the power source of energy was made by William Gilbert. A great number of further important discoveries were made over the next two centuries – among them are a light bulb and electromagnetic induction principle. The start of the electrical industry began in 1881 when the first power station in the world was constructed at Godalming in England. Then in 1882 the great inventor Thomas Edison and his Edison Electric Light Company started their first steam-powered station in New York. That was the beginning of the new era of electricity that changed the way people lived. By 1890 there were thousands of power systems in Europe and the USA.
Развитие электричества началось еще в 17 веке, и сделано было открытие этого источника энергии Уильямом Гилбертом. Огромное количество дальнейших важных открытий было совершено за последующие два века - среди них были лампочка накаливания и принцип электромагнитной индукции. Начало промышленному производству электричества было дано в 1881 году, когда была возведена первая электростанция в английском Годалминге. Затем в 1882 году великий изобретатель Томас Эдисон и его компания запустили паровую электростанцию в Нью-Йорке. Это стало началом новой эры электричества, которая изменила образ жизни людей. К 1890 году в Европе и США работали уже тысячи электростанций.
But what is the electricity? From the scientific point of view, the electricity is a particular set of physical phenomena which is characterized by the presence and the distinctive flow of electric charge. It is created when the small particles – electrons move between the atoms. This process creates an electric current. And this current is used to energize different kinds of equipment. Electrical Power Industry can be fair enough called a backbone of the modern industry and everyday life.
Но что же такое электричество? С научной точки зрения, электричество - это определенный набор физических явлений, который характеризуется присутствием и определенным течением электрического заряда. Создается электричество, когда маленькие частицы - электроны перемещаются между атомами. Этот процесс создает электрический ток. И этот ток используется в качестве энергии для различных видов механизмов. Электроэнергетика, без сомнения, является становым хребтом современной промышленности и повседневной жизни.
We use electrical power for heating, cooling and lighting our houses, for cooking food, and for numerous devices and gadgets such TV-sets, computers and smartphones. Electrical power has become the essential necessity for the modern society. But unfortunately not all people in the world have an access to this source of energy. Millions of people in poor countries have to survive without the advantages of electrical power.
Мы используем электрическую энергию для отопления или охлаждения наших домов, приготовления пищи и для бесчисленного множества устройств и гаджетов, таких как телевизоры, компьютеры или смартфоны. Электрическая энергия стала одним из необходимых слагаемых современного общества. Но, к сожалению, не все жители планеты имеют доступ к этому источнику энергии. Миллионы людей в беднейших странах вынуждены выживать без преимуществ электроэнергии.
Besides the obvious advantages that electrical power brings to our life there is a definite set of threats that this modern technology causes. The process of electricity generation on different kinds of power stations often is not so harmless to the nature. One of the most efficient but dangerous means of electricity generation is a nuclear power station. Though this is one of the most effective ways to generate electricity for the needs of the society, the disastrous catastrophes in Chernobyl and Fukusima showed us how dangerous nuclear power is.
Устройства для передачи крупных мощностей электр. энергии из мест ее производства на большие расстояния в места потребления. Л. э. состоят из медных, алюминиевых или стале алюминиевых проводов, либо подвешиваемых посредством изоляторов к… … Технический железнодорожный словарь
Красные линии - границы, отделяющие земли (территории) общего пользования в населенных пунктах от иных видов земель, а также обозначающие земельные участки, на которых расположены сети инженерно технического обеспечения, линии электропередач, связи, трубопроводы … Большой юридический словарь
Линия электропередач - Линии электропередачи Линии электропередачи город Шарья Линия электропередачи (ЛЭП) один из компонентов электрической сети, система энергетического оборудования, предназначенная для передачи электроэнергии. Согласно МПТЭЭП (Межотраслевые правила … Википедия
Опора линии электропередачи - Гиперболоидная опора мостового перехода ЛЭП НИГРЭС через Оку в пригороде Нижнего Новгор … Википедия
линейная - 98 линейная [нелинейная] электрическая цепь Электрическая цепь, у которой электрические напряжения и электрические токи или(и) электрические токи и магнитные потокосцепления, или(и) электрические заряды и электрические напряжения связаны друг с… …
Авария на АЭС Фукусима I - Тип Радиационная авария Причина Землетрясение, цунами … Википедия
Авария на АЭС Фукусима-1 - Авария на АЭС Фукусима I Тип Радиационная авария … Википедия
СП 11-112-2001: Порядок разработки и состав раздела "Инженерно-технические мероприятия гражданской обороны. Мероприятия по предупреждению чрезвычайных ситуаций" градостроительной документации для территорий городских и сельских поселений, других муниципальных образований - Терминология СП 11 112 2001: Порядок разработки и состав раздела "Инженерно технические мероприятия гражданской обороны. Мероприятия по предупреждению чрезвычайных ситуаций" градостроительной документации для территорий городских и… … Словарь-справочник терминов нормативно-технической документации
Монтаж лэп под тяжением - Метод монтажа ЛЭП Под тяжением современный метод монтажа Линий Электропередач без раскатки провода по земле. Содержание 1 Технология 2 Виды техники для монтажа ЛЭП … Википедия
Трансформатор - У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Трансформатор (значения). Трансформатор силовой ОСМ 0,16 Однофазный сухой многоцелевого назначения мощностью 0.16 кВт … Википедия
МЭС Центра - Тип Филиал ОАО «ФСК ЕЭС» Год основания 1954 Расположение … Википедия
Книги
- Основные вопросы проектирования воздушных линий электропередач. Учебное пособие , Ф. Р. Исмагилов, Р. Г. Шакиров, Н. К. Потапчук, Т. Ю. Волкова. Главное внимание уделено конструкции проводов и опор воздушных линий электропередач, анализу статической работы сталеалюминиевых проводов и различных режимов работы провода воздушной линии,… Купить за 1291 руб
- Электроэнергетика России. Плакат , . Масштаб 1:6 000 000. Значками разных цветов на карте изображены электростанции по виду используемой первичной энергии: тепловые, гидроэлектростанции, атомные, геотермальные. Размер значка… Купить за 492 руб
- Воздушные линии электропередач, подвесные энергетические системы и магистральные трубопроводы , В.А. Котляревский. В книге предпринята попытка представить в доступной для инженера форме методы и средства оценки ресурсов прочности воздушных линий электропередач, подвесных энергетических систем и…